PHYSICAL EXAMINATION:
Blood pressure 102/80; pulse 128; respiratory rate 32; oral temperature 37.0 C.
GEN:
She appears to be in moderate
respiratory distress. She is well
developed and nourished.
HEENT: There is no tracheal
deviation.
CV:
Examination of the heart
revealed an accentuated pulmonic component of the second sound.
PULM:
Her breathing is rapid and
shallow. There is dullness to
percussion and decreased breath sounds in
the left base. There were no
rhonchi or crackles or sounds of increased
voice transmission.
ABD:
The abdomen, pelvic and rectal exams
were normal.
EXT:
The extremities showed no edema, cyanosis or clubbing.
The shoulders revealed normal range
of motion; no warmth or tenderness was noted.
The other joints are normal.
LABORATORY TESTS:
The
emergency room physician orders the following tests:
CBC:
\
15
/
140 |
105 |
10 /
11.5 -------------
------------------------ 85
/
43 \
3.8
|
24 |
0.7 \
(83 polys, 1 band, 14 lymphs).
Blood
Gases:
FIO2
pH
PCO2
PO2
0.21
7.48
30
80
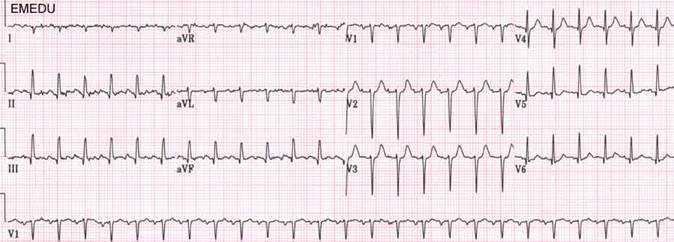
EKG:
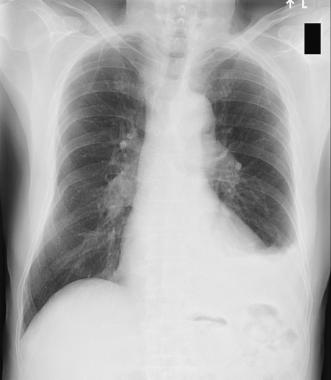
CXR is done
a)
Unfractionated heparin
infusion
b)
Low molecular weight
heparin
c)
Warfarin (Coumadin)
d)
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
e)
Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
f)
Aspirin
Fill in the “recommended duration of anticoagulation” for each of the VTEs
mentioned below:
|
|
Risk of recurrence after 1 year |
Risk of recurrence after 5 years |
Recommended duration of anticoagulation |
|
VTE provoked by surgery: |
|
|
|
|
VTE provoked by nonsurgical reversible factor (estrogen, pregnancy,
leg injury, flight >8hrs): |
|
|
|
|
Unprovoked VTE |
|
|
|
|
Provoked VTE with persistent risk factor (antiphospholipid syndrome
or other inherited thrombophilias) |
|
|
|
|
VTE in setting of cancer |
|
|
|
|
Unprovoked isolated distal DVT |
|
|
|
A. Systemic Thrombolysis
B. Catheter-directed thrombolysis
C. Anticoagulation with Lovenox or DOAC (Apixiban)
|
C |
|
A |
|
B |
|
C |
|
A |
18. What would you tell the patient to do to prevent future DVT and PE?
The patient is discharged home on your recommended therapy. She returns to the ER 10 days later with coffee ground emesis. Her hemoglobin has dropped from 15 g/dL to 10g/dL.
19. What can you do if the patient has a major contraindication to the standard therapy for DVT/PE?
·
Antithrombotic Therapy for
VTE Disease, 10th ed: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines.
CHEST 2016;149 (2)
·
Acute
Pulmonary embolism.
NEJM 2010; 363:266-274.
·
Duration
of anticoagulant therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Blood. 2014 Mar 20;123(12):1794-801
·
SIMPLE
Case # 30. MedU portal.