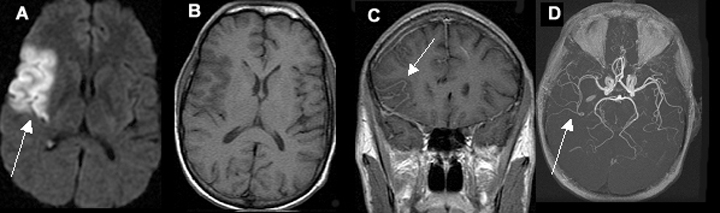
Acute One Day Old Infarction Involving the Right Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Territory
A. Diffusion weighted image shows area of infarct as bright signal.
B. T1 image shows no evidence of blood in the area of infarct (blood would appear as white).
C. Post contrast coronal image shows vascular enhancement in the area of infarct.
D. MR angiography shows right middle cerebral artery branches to be narrower in calibre, as compared to left.