MRI is the imaging procedure of choice for diagnostic investigation of MS.
MRI flair images are sensitive in identifying MS lesions.
Multiple sclerosis plaques occur in the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres, brain stem and spinal cord.
Lesions are asymmetrical in periventricular and subcortical areas. Periventricular white matter lesions that are perpendicular to the lateral wall of lateral ventricles (Dawson's finger) are characteristic of MS and distinguishes from other white matter lesions.
Peripheral white matter MS lesions are seen near the gray matter white matter junctions.
They are seen as bright lesions on T2 weighted or FLAIR MR images.
Acute lesions may enhance.
The bright MRI lesions of MS may be impossible to distinguish from subcortical infarctions, so clinical knowledge of the patient is crucial. Typical lesions occur in space and time (past history of similar episodes )
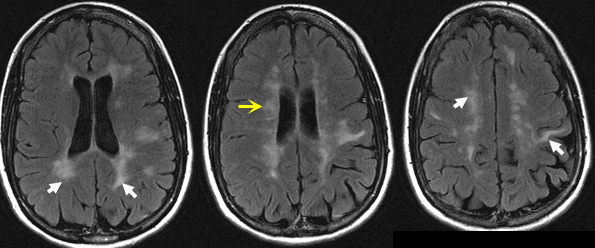
Case:
37 year old female presents with blurry left eye.
Past history of paraperesis.
FLAIR images show asymmetrical, abnormal high signal white matter lesions in the periventricular and subcortical areas (white arrows).
Yellow arrow is pointing to lesions around the ventricles (Dawson's fingers).
Etiology for white matter lesions:
- White matter infarcts secondary to microvascular disease with predisposing factors that include:
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia
- Vasculitis
- Multiple sclerosis
- HIV related infections
- HIV encephalitis
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Radiation induced leukoencephalopathy
- Chemotherapy induced leukoencephalopathy