Case Answers:
Answer 1
Category of shock |
Physiologic abnormality |
Distributive |
Decreased systemic vascular resistance |
Cardiogenic |
Decreased contractility |
Hypovolemic |
Decreased preload |
Obstructive |
Obstruction to filling (tamponade) or obstruction to forward flow (massive PE or HTN emergency) |
How might these 4 categories of shock be further separated into two physiologic patterns?
- High vs low cardiac output
- MAP = CO x SVR
- CO = HR x SV
- SBP-DBP = pulse pressure
- High cardiac output (warm, well perfused, bounding pulses, wide pulse pressure) = distributive
- Pulse pressure (PP) is surrogate for stroke volume à Wide PP = High SV
- Low CO (cool, thready pulses, narrow PP) = hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive
Finally, how might you determine which type of shock is present in any given patient?
- Physical exam: assess pulses, skin temp, capillary refill
- History
- Swan Ganz Catheters are no longer routinely used though can be used in mixed shock states
- Flow Track Monitors: in the perfect patient (passive on vent, 8cc/kg Vt, normal sinus rhythm) have excellent sensitivity and specificity for predicting volume status
- Bedside echo to assess cardiac function, IVC collapsibility (variable based on operator and only reliable in a passive patient on the ventilator)
- Overall, it is important to rely upon one’s clinical skills with judicious use of technology to help support and/or rule out clinical hypotheses.
Answer 2
Septic (wide pulse pressure, warm extremities, bounding pulses, capillary refill).
- Define SIRS, sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock based on the Surviving Sepsis guidelines
SIRS |
SEPSIS |
SEVERE SEPSIS |
SEPTIC SHOCK |
T >38 or <36
RR >20 or pCO2<32
HR>90
WBC >12 or <4 or >10% bands
|
SIRS plus documented suspicion or evidence of infection |
Sepsis plus evidence of impaired end organ perfusion:
Elevated lactate>2
AKI
- Oliguria (<0.5cc/kg/hr)
- Cr > 2
AMS
Hypotension
- SBP < 90
- MAP< 65
- SBP > 40 from baseline
Hypoxia
- O2 sat < 90%
- Increasing O2 req
Coagulopathy
- PTT > 60 sec
- INR > 1.5
- Platelets < 100,000
Bilirubin > 2 |
Severe sepsis with persistent hypotension despite crystalloid fluid resuscitation (30cc/kg) OR
Lactate >4
|
- Recent JAMA article (Feb 2016) presented new sepsis definitions:
- Sepsis: infection + acute change of >2 points in SOFA score
- Septic shock: sepsis + hypotension unresponsive to fluids + pressors to keep MAP>65 + lactate >2mmol/L
- Note that SIRS is no longer recommended by this group as a screen for sepsis
Answer 3
Blood and urine cultures, broad spectrum antibiotics and IVF
- Lack of proven benefit to colloids compared to crystalloid.
- Septic shock patients usually require a large volume of fluid (6-8L), even those with a history of CHF, ESRD or cirrhosis
- Recent papers (Process, Promise and Arise) found that targeting CVP and/or SvO2 in septic shock do not lead to improved mortality and thus are no longer recommended
- 3 hour bundle recommended by CMS includes blood culture, antibiotics and lactate along with fluids (30cc/kg) if hypotensive or if lactate >4
What lab value can be used as a marker of tissue hypoxia and also correlates with patient mortality?
Lactate
- Higher lactate correlates with higher mortality
- Included in both definitions for septic shock (JAMA uses >2mmol/L, surviving sepsis uses >4mmol/L)
- Sepsis is not the only situation which leads to an elevated lactate (all types of shock, cancer (leukemia/lymphoma), liver disease decreases clearance, metformin, propofol, albuterol, epinephrine, etc)
- The use of lactate clearance to monitor and guide therapy remains under investigation
If you measured an mixed venous O2 saturation in this patient, would you expect it to be high, low or normal?
- SvO2 (mixed venous saturation) gives you an idea of O2 delivery and O2 consumption
- Normal O2 delivery (DO2) = 1000ml/min
- DO2 = CO x CaO2
- CaO2 = (1.34 x hgb x O2 sat) + (PaO2 x 0.0031) = ~20ml/dL
- Normal O2 consumption (VO2) = 250ml/min
- Normal SvO2 =75%
- Causes of ↓SvO2
- ↓O2 delivery: decreased CO, decreased hgb, decreased O2 sat
- ↑O2 consumption: extreme fever, pain, WOB
- Can be high, low or normal in septic shock depending on cardiac output and degree of tissue dysfunction
- SvO2 classically high or normal in septic shock but low in cardiogenic or hypovolemic shock
Will your initial therapeutic intervention vary significantly based upon what category of shock is present?
- Not in most cases. Regardless of the etiology of shock, initial resuscitation should include IV fluids. One might choose a smaller initial volume/flow rate for cardiogenic shock; however, most patients with cardiogenic shock will benefit from the administration of some IV fluids to optimize the patient’s position on their Starling curve.
Answer 4
Approximately 43 mmHg (MAP = DBP + (SBP - DBP)/3).
Answer 5
- ΔP/Δflow = MAP-RAP/CO x 80 = 43-3/5 = 8 x 80 = 640 dyne-sec/cm5
- ΔP/Δflow = mPAP-wedge/CO x 80 = 15-10/5 = 1 x 80 = 80 dyne-sec/cm5
- SVR: 900-1400
PVR: 150-250
Answer 6
ARDS and multisytem organ failure (MSOF).
Answer 7
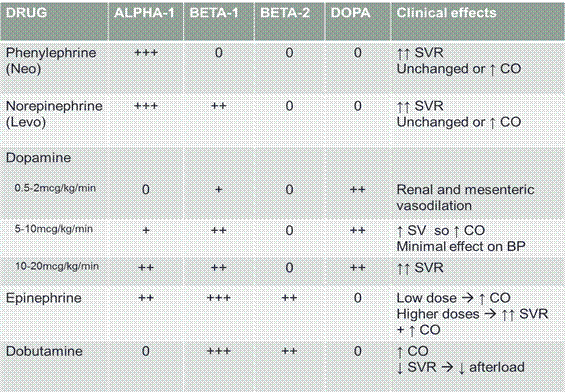
“Effective” dosing ranges:
Phenylephrine 0.05-9 mcg/kg/min
Norepinephrine 0.01-2 mcg/kg/min
Epinephrine 0.01-0.5 mcg/kg/min
Dobutamine (2.5-10 mcg/kg/min)
- Norepinephrine (SOAP II NEJM 2010)
- Central line preferred, peripheral administration of low concentration acceptable for 2-4 hours pending central line placement, decreases risk of extravasation
- Norepinephrine 0.01-2 mcg/kg/min effective dose in sepsis (1-20 mcg/min in non-weight based)
- MAP>65 (discuss MAP 65 vs higher MAP goals)
- Arrhythmias (management – treat arrhythmia vs adding or switching to agents that will lessen the chronotrope effects of norepi)
Ischemia (limbs, heart, mesenteric bed – renal failure, ischemic bowel)
Answer 8
Corticosteroids
- Stress the high incidence of adrenal insufficiency in patients with septic shock (NEJM 2008) and therefore random cortisol and cort stim tests no longer recommended
- No difference in mortality in those who receive steroids but faster recovery from shock than those who receive placebo
Vasopressin
- Vasopressin levels are often depressed in patients with septic shock
- VAAST trial (NEJM 2008): no difference in mortality in those who received vaso + levo compared to levo alone but lower incidence of arrhythmias because vaso allowed lower dose of levophed
- If added, start 0.04 units/min, wean other pressors off, then wean/stop vasopressin (less rebound hypotension if order of pressors is done this way
Methylene blue
- Decreased vascular tone is due to proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide production
- Nitric oxide diffuses across cell membranes, activating guanylate cyclase, which converts guanosine triphosphate to cyclic cGMP which causes smooth muscle relaxation
- Methylene blue is a selective inhibitor of guanylate cyclase
- Consider MB in patients who remain hypotensive despite receiving multiple agents
- Kirov MY, Evgenov OV, Evgenov NV, et al. Infusion of methylene blue in human septic shock: a pilot, randomized, controlled study. Crit Care Med 2001;29:1860–7.
- All patients received either methylene blue as an intravenous bolus injection of 2 mg/kg over 15 minutes followed 2 hours later by a continuous intravenous infusion at stepwise increasing rates of 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 mg/kg/hour maintained for 1 hour each (10 patients), or placebo (10 patients).
- At 6 hours after the start of the infusion, methylene blue significantly
- Increased mean arterial pressure (MAP)
- Increases in systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
- Reduced pressor requirement
- Effect lasted 24 hrs
- Clinical outcomes (duration of shock or mechanical ventilation, number of organ dysfunctions, fluid administration, sedation requirements, and ICU or hospital length of stay) were not significantly different between groups.
- There was also no difference in 28-day survival between groups.
Answer 9
|
CVP |
PCWP |
CO |
SVR |
SvO2 |
Septic |
Low |
Low |
High |
Low |
High or normal |
Cardiogenic |
High |
High |
Low |
High |
Low |
Hypovolemic |
Low |
Low |
Low |
High |
Low |
Obstructive
(massive PE) |
High |
Low |
Low |
High |
Low |
Answer 10
- Cardiogenic shock complicates 7-10% of acute MI = 60-80% mortality
- SHOCK trial NEJM 1999
- Acute MI with shock randomized to medical stabilization vs early revascularization (within 6 hours)
- Early revasc had better outcome 47% vs 34% 1 year survival
- IABP
- Balloon inflates before QRS (during diastole) and deflates right after QRS (during systole)
- Increases MAP, decreases SVR/afterload, inc myocardial O2 supply and dec O2 demand
- Increases diastolic blood flow into coronary vessels
- available evidence does not support the routine use of an IABP in most patients with acute MI complicated by cardiogenic shock in whom primary PCI is attempted or performed or in whom fibrinolytic therapy is administered.
- However, benefit may exist in patients with mechanical defects (such as mitral regurgitation or a ventricular septal defect) or if rapidly deteriorating
- IABP-SHOCK II trial NEJM 2012)
- 600 patients with shock complicating acute MI were randomly assigned to the device or no device.
- All patients were expected to undergo early revascularization (predominantly with PCI) and to receive best available medical care.
- At 30 days, there was no difference in the rate of all-cause mortality (39.7 versus 41.3 percent)
- Discuss potential good and bad effects of dobutamine and milrinone
- these drugs do not reverse the hypotension in post-MI shock, which is sometimes accompanied by vasodilation rather than vasoconstriction.
- Dobutamine (increases O2 demand > O2 supply so increased O2 consumption) +/- levophed (if hypotensive)
- May be used in less sick pts with low CI and high PCWP but without severe hypotension
- Milrinone increases O2 supply and O2 demand so no change in O2 consumption

