Osteoporosis
Objectives:
Upon completion of this unit, you will be familiar with:
- Imaging procedures considered for early detection of osteoporosis
- Mechanism and limitation of bone densitometry scan
- Radiological criteria for osteoporosis
- Sensitivity and specificity of bone densitometry studies
- Identification of high risk individuals
- Annual screen
- Cost for population screening
- cost per procedure
- number of potential subjects
- Morbidity advantage of early detection
What is osteoporosis?
- Decrease in bone matrix
- Mineralization is preserved
What are the risk factors for osteoporosis?
Risk factors for osteoporosis include:
- Age
- Long term use of steroids
- Smoking
How do patients with osteoporosis present or when would you suspect osteoporosis?
- Loss of height with aging
- Kyphosis with aging
- Compression fractures of vertebra
- Be suspicious of osteoporosis in a patient exhibiting the following signs:
- Any fracture after age 40
- Adult weighing less than 125lbs
- Fracture of wrist, spine or hip in first-degree relative after age 50
What are the commonly used types of peripheral bone density measurements and how do they compare? Which is the gold standard?
Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA):
- Posteroanterior lumbar spine and proximal femur
- X-rays with two energy peaks are produced, allowing diff. absorption of radiation by bone and soft tissue, from which BMD (bone mineral density) is calculated
- GOLD STANDARD
Quantitative CT (QCT):
- Lumbar spine
- Unique in that it measures trabecular bone density
- Probably the most sensitive test in measuring changes in bone density, however it is not as precise as DXA and it is not as widely used because of higher radiation dose.
What bone density measurement site correlates best with clinically important fractures?
- The hip is the best site for predicting clinically important fractures.
- Relative risk of fracture per 1 SD change
 |
| What is a T-score?
T-SCORE = the number of standard deviations the bone mineral density measurement is above or below the YOUNG (30 year old)-NORMAL MEAN bone mineral density.
Patients BMD - Young adult Mean BMD / Standard deviation of young adult BMD
I see various baseline standards used for BMD : 30 year old, 25-35 year olds, same sex, both sexes, same ethnicity etc.
What is a Z-score?
Z-SCORE = the number of standard deviations the measurement is above or below the AGE -MATCHED MEAN bone mineral density.
Patients BMD - Peer age group Mean BMD / Standard deviation of peer age group BMD
How do you use T and Z scores in clinical decision?
Standards are established only for women. We just use the same standards arbitrarily for men.
T-Score is the standard used to determine the risk for fractures. 30 year old BMD is considered the baseline for comparison. BMD decreases with age and becomes less stronger.
A bone mineral density more than 2.5 standard deviations below the mean for a young healthy adult white woman identifies 30 percent of all women as having osteoporosis; half of these women will already have had a fracture.
- -1 to +1 is normal range
- -1 to -2.5 is osteopenia
- -2.5 is osteoporosis
The hip T-score is the site used in clinical decisions.
Z-score is used to determine whether the BMD is less than the age related bone loss. This would call for investigation of causes of osteoporosis unrelated to age. Z-score is helpful in identifying persons who should undergo a work-up for secondary causes of osteoporosis.
Visual photo of spine or hip is used for comparison when sequential studies are done.
|
Case 1
A postmenopausal 53-year-old white woman comes to clinic for an annual physical. Her exam is normal. She has come across many advertisements regarding osteoporosis screening. What would you recommend?
A: Order bone mineral density scan
B: Empiric preventive treatment for osteoporosis
C: Need more clinical information prior to giving recommendations
Answer: C
For women over the age of 50 and under 65, you need at least one risk factor to recommend bone mineral density scan.
Case 2:
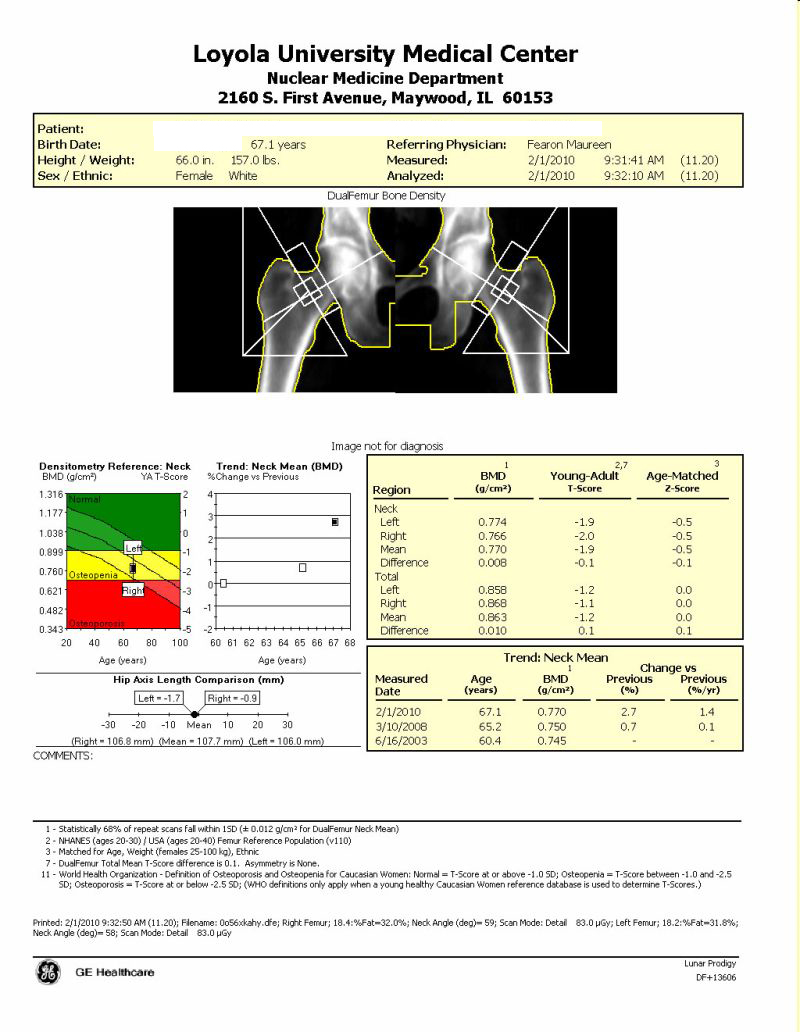
A 66 y/o white female comes to the clinic for routine follow up. She is concerned about osteoporosis and being that she is over 65, she qualifies for a bone mineral density scan. A DXA shows total hip bone mineral density 0.93 SD above the 66-year-old mean and 0.36 SD below the 25-year-old mean. T score is reported as -036 and her Z score is 0.93.
What is a T-score?
T-SCORE = the number of standard deviations the bone mineral density measurement is above or below the YOUNG (30 year old)-NORMAL MEAN bone mineral density.
Patients BMD - Young adult Mean BMD / Standard deviation of young adult BMD
What is a Z-score?
Z-SCORE = the number of standard deviations the measurement is above or below the AGE -MATCHED MEAN bone mineral density.
Patients BMD - Peer age group Mean BMD / Standard deviation of peer age group BMD
How do you use T and Z scores in clinical decision?
How do you use T and Z scores in clinical decision?
A bone mineral density more than 2.5 standard deviations below the mean for a young healthy adult white woman identifies 30 percent of all postmenopausal women as having osteoporosis; half of these women will already have had a fracture.
- -1 to +1 is normal range
- -1 to -2.5 is osteopenia
- -2.5 is osteoporosis
The hip T-score is the site used in clinical decisions. It is used in pre menopausal women.
Z-score is less commonly used but may be helpful in identifying persons who should undergo a work-up for secondary causes of osteoporosis. Z-score is is useful in post menopausal women.
The hip T-score is the site used in clinical decisions.
A Z-score changes over time in relation to the T-score.
Converting T-score to Z-score at the hip:
- Age 50: T = Z - 0.37
- Age 60: T = Z - 1.01
- Age 70: T = Z - 1.56
- Age 80: T = Z - 2.11
- Age 90: T = Z - 2.52
What factors contribute to the estimate of the annual cost of screening all potential subjects in United States?
Cost of the program depends on:
- Number of women over 65
- Number of women between 50-65 with risk factor
- Cost of DXA
How do you justify the cost of annual screening for osteoporosis?
- Prevention of morbidity due to vertebral fractures.
