|
|
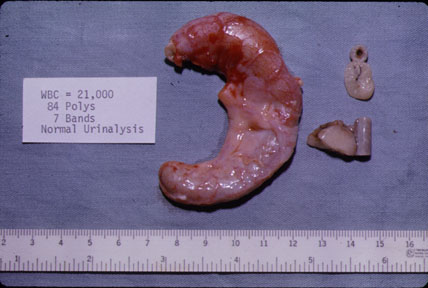
The appendix is markedly swollen. The serosa is hyperemic and covered by a fibrinous exudate. Compare the inflamed appendix to the adjacent segments of a normal appendix. |
| Pathology | Imaging |
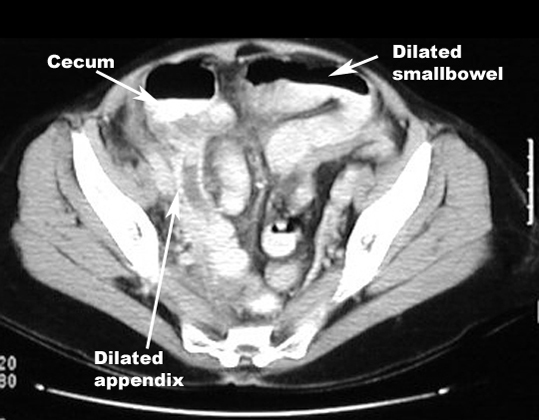
| The appendix is inflamed. The lumen is filled with neutrophils. The mucosa is ulcerated. | Appendix measures 7 mm or more Abnormally distended appendix Thick-walled appendix
Appendix is not compressible on ultrasound. |
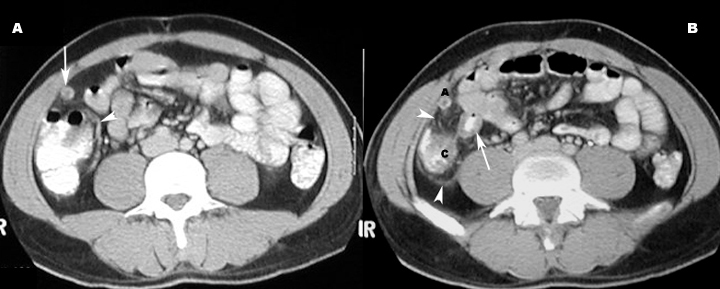
| There is inflammation of visceral and parietal peritoneum. | Ileus: Dilated loops of bowel
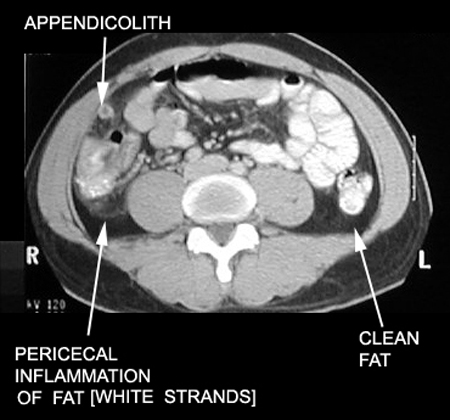
Periappendiceal inflammation/inflammatory infiltration of fat Free fluid in cul de sac Cecal thickening Pericecal lymphadenopathy.
|
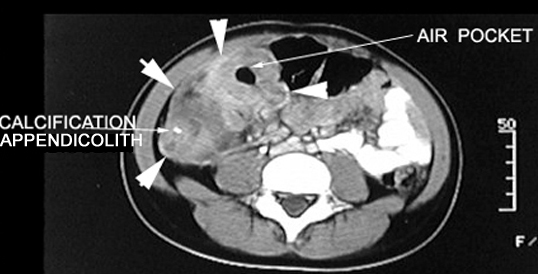
| Appendiceal inflammation is associated with obstruction in 50 to 80% of cases (due to fecolith, tumor or ball of worms - Oxyuriasis vermicularis). | Appendicolith |
| Complications | |
|
Free air in abdomen |
|
|
|
Inflammatory mass, air pockets, contrast enhancement |
|
Diagnosis of appendicitis is based on clinical picture and imaging studies can be normal |
|