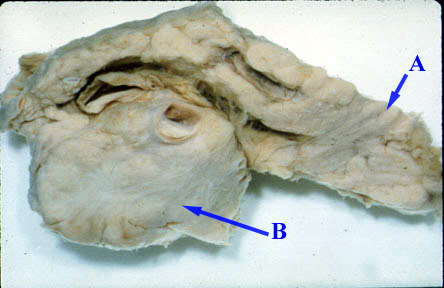
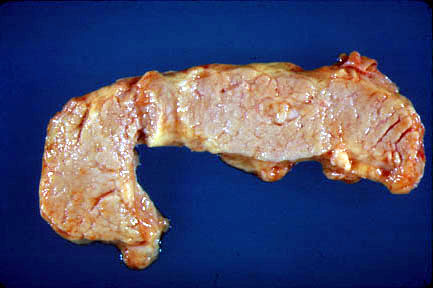
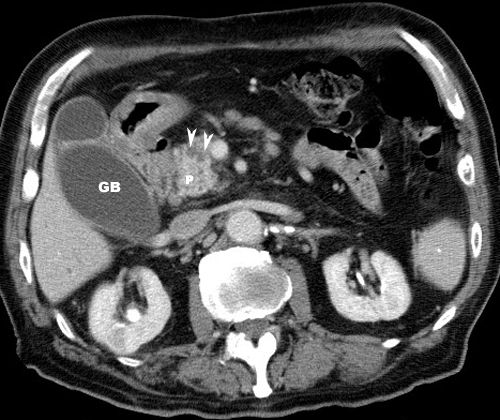
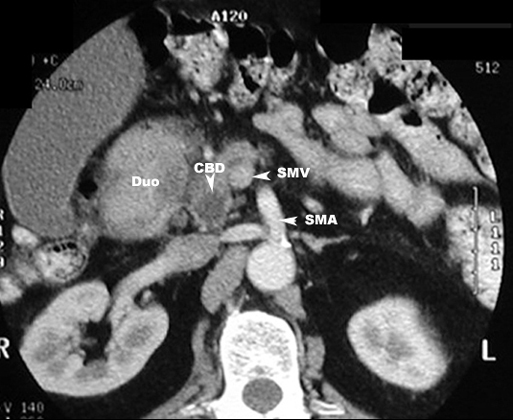
- The neoplasm and extensive fibrosis replaces
most of the normal pancreas.
- Tumor can be located anywhere in pancreas.
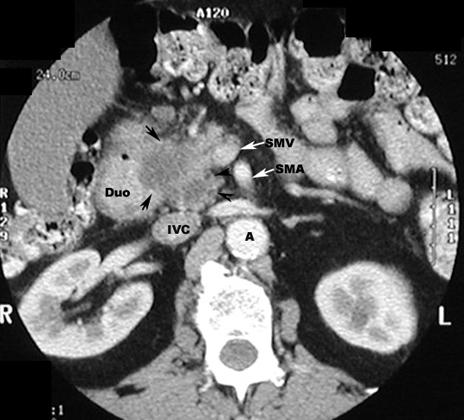
- The neoplasm, in the head of the
pancreas, can compress the common bile duct causing an extra
hepatic obstruction.
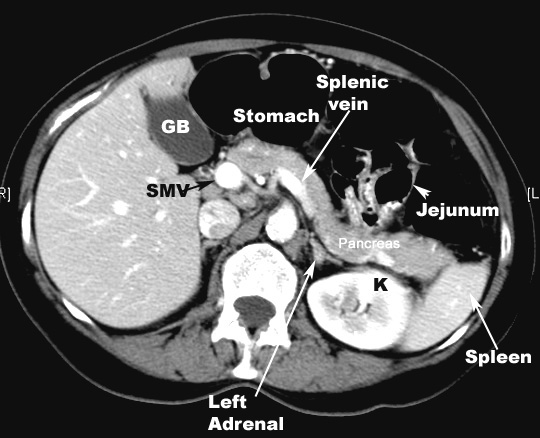
- Dilatation of intrahepatic bile
ducts, common bile ducts (CBD) and gallbladder (Courvoisier
GB).
- Cancer in the tail of pancreas may
obstruct the splenic vein or cause a mass effect on adjacent
structures.
|
- Mass
- Biliary tract obstruction when the carcinoma
is in the head.
- Dilatation of intrahepatic bile
ducts, common bile ducts [CBD] and gallbladder.
- Courvoisier GB
- Cancer in the tail of pancreas may obstruct
the splenic vein or cause mass effect on adjacent structures
|