 |
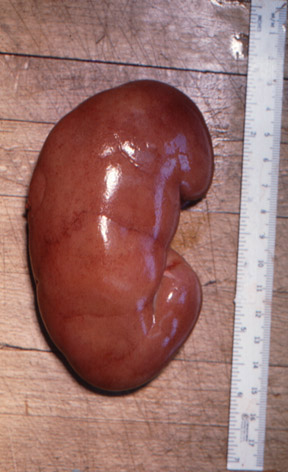 |
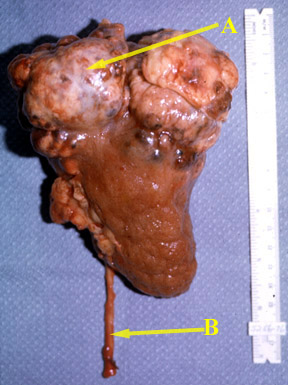
| The surgical specimen consists of a whole kidney and attached ureter (B). There is a large, irregular carcinoma (A) in the superior pole of the kidney. | Normal kidney |
Renal masses
| Common Renal Masses | Imaging |
| Simple renal cysts:
Most common in patients over 50 years of age. These cysts are typically asymptomatic. |
CT: Well defined mass with water [low] density
usually in the renal cortex. U.S Well marginated mass with no internal echoes and posterior enhancement indicating fluid. |
Polycystic kidney disease:
A positive test requires:
|
Kidneys are large in polycystic kidneys. |
| Abscess | Collection air and fluid pockets |
| Renal cell carcinoma |
|
 |
 |
| The surgical specimen consists of a whole kidney and attached ureter (B). There is a large, irregular carcinoma (A) in the superior pole of the kidney. | Normal kidney |
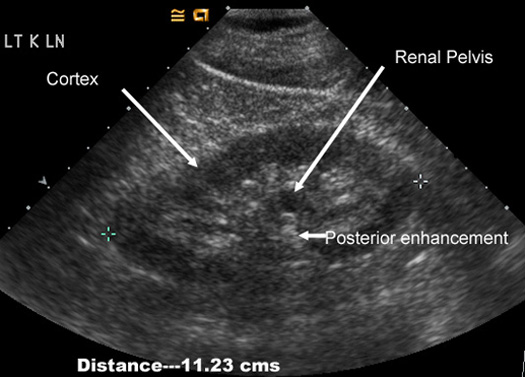 |
Normal kidney in US: Measures 9-11 cms Has the same extent of echoes as liver Cortex measures about 2.5 cms Central echoes are from fat surrounding renal pelvis. Renal pelvis is filled with urine and is echo free. Note the posterior enhancement behind renal pelvis.
|
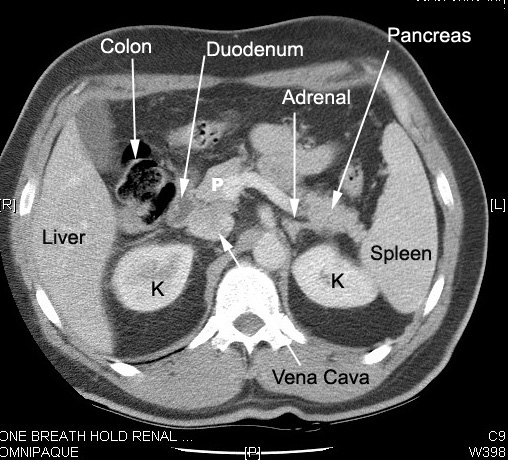 |
Normal kidney in CT: Located in retro peritoneum surrounded by fat. Renal cortex enhances with IV contrast. In the nephrographic phase the contrast has not been excreted and the renal pelvis appears dark. Renal pelvis and ureters can be seen as the contrast is excreted by kidneys. Note the relationship of kidneys Renal veins drain into IVC.
|
Following are examples of renal mass in imaging procedures:
 |
CT scan in a patient with Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
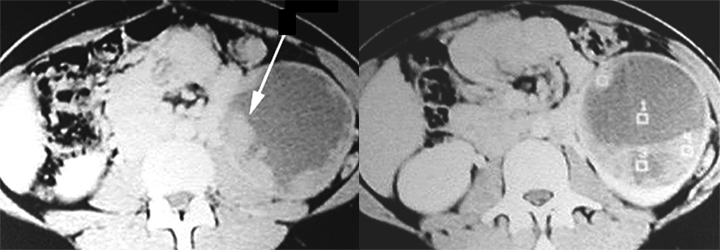 |
CT scan in another patient with Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
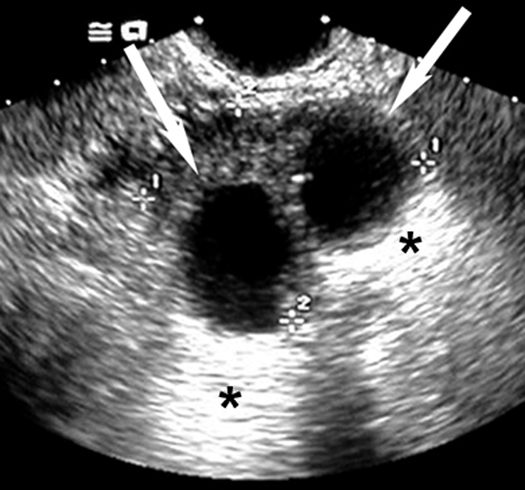 |
Renal CystsUltrasound can easily distinguish renal cysts from mass lesions.Simple Anechoic Renal CystsArrows points to cyst. * Points to good through transmission of echoes behind the cyst. |
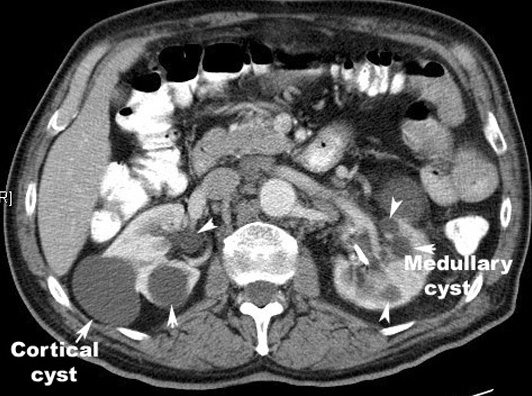 |
Multiple renal cysts |
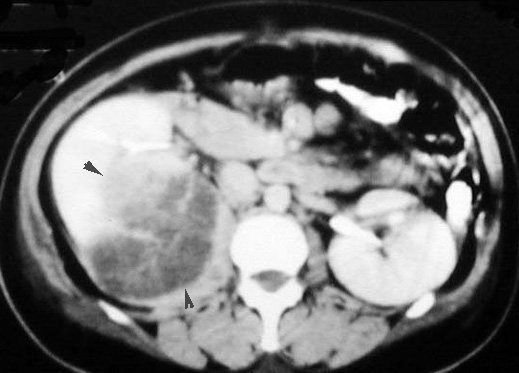 |
Renal Abscess Large low density mass within the parenchyma of right kidney, with a crescentic rim of renal parenchyma posterior to the abscess.
|