Renal masses / Renal cancer
What are the common causes of renal masses?
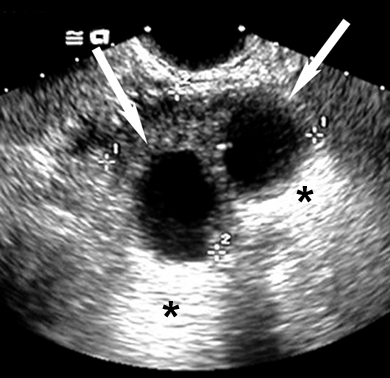
- Simple renal cysts: Most common in patients over 50 years of age. These cysts are typically asymptomatic.
- Polycystic kidney disease: A positive test requires:
- in patients younger than 30 years of age, at least two cysts (unilateral or bilateral)
- in patients 30-59 at least two cysts in each kidney
- in patients over 60, four or more cysts
- Abscess
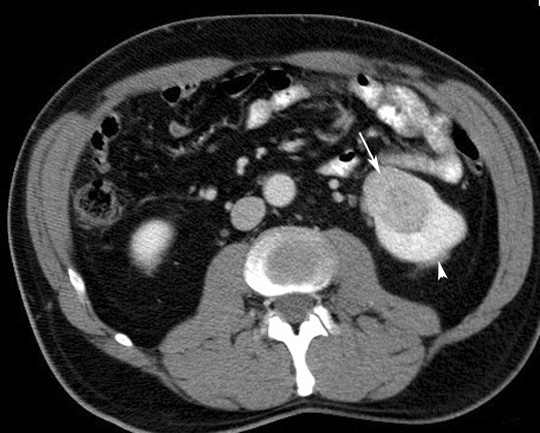
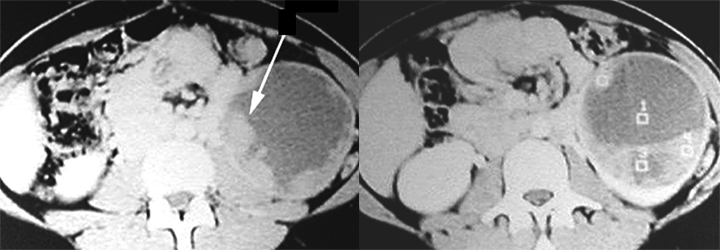
- Renal cell carcinoma
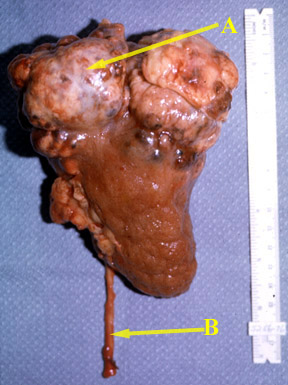
Normal kidney