Spinal Cord Compression and tumors
What are the available imaging procedures for evaluation of spinal cord compression and their utility?
- Sagittal MRI images of the entire spinal cord should be done so other subclinical lesions are not missed.
- MRI is the best imaging technique to evaluate patients with spinal cord compression.
- CT myelography is an alternative if MRI cannot be done, but requires lumbar puncture and instillation of contrast.
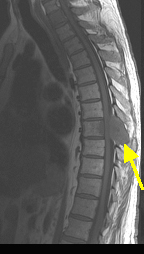
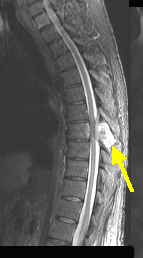
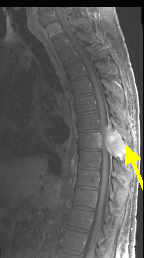
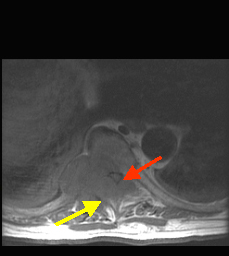
Case 1:
A 73 y/o male with a history of kidney cancer presents to the ER with weakness of his lower extremities, and incontinence early today. He also complains of severe lower back pain. On exam, the patient is found to have increased deep tendon reflexes and spastic paralysis, of both lower limbs, with absent pinprick and temperature sensation in the lower limbs up to the umbilicus.
Which imaging procedure will you order?
Emergency MRI of spine
What is your clinical diagnosis?
Spinal cord compression from metastatic disease.
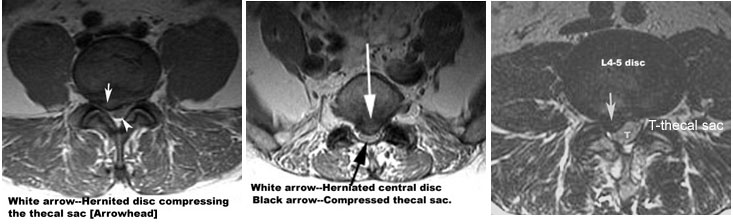
Case 2:
A 68 year old male presents with shooting pain along the back of right leg. He has been having back ache for the past 6 months. His sensation and strength are intact but the right ankle reflex is absent.
Which imaging procedure will you order?
MRI of lumbar spine
What is your clinical diagnosis?
R S1 radiculopathy from degenerative arthritis or herniated disc.
|
Osteoarthritis Herniated Disc |