 |
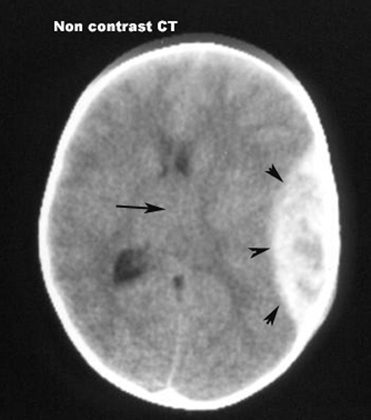
CTEpidural Hematoma
|
Acute hematoma is seen by non-contrast imaging as an area of high density. CT can detect acute intracerebral blood as small as 2mm, due to contrast between high density of blood and low density of surrounding brain.
 |
CTEpidural Hematoma
|
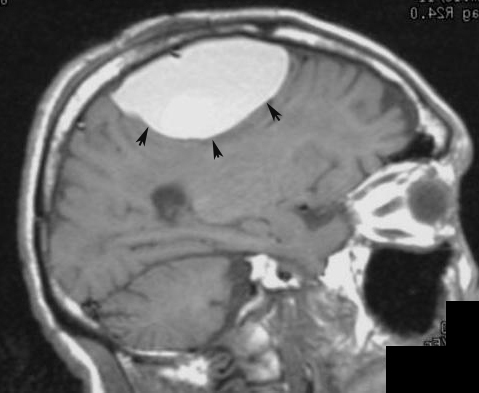 |
MRIEpidural Hematoma |
|
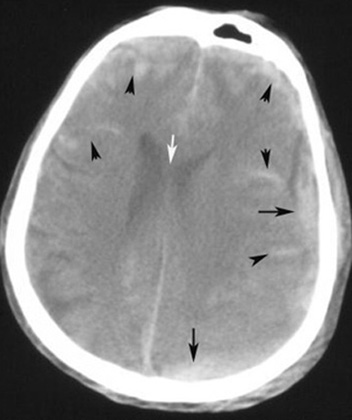
Diagnosis: Acute Subdural Hematoma
Patient with history of recent fall. |
|
|||
Diagnosis: Chronic Subdural Hematoma55 year-old patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia with low platelet count.
|
 |
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage / Subdural Hemorrhage
|
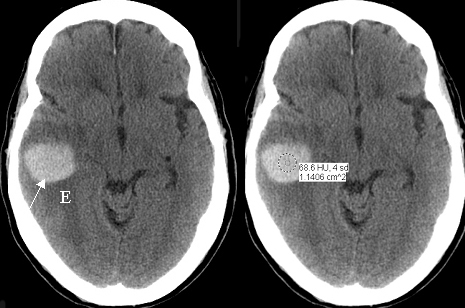 |
Diagnosis: Acute Intracerebral HematomaAcute intracerebral hematoma within the right temporal lobe (arrow) with surrounding edma (E). 60 year-old patient with melanoma. Hemorrhage is from metastatic tumor bleed. Acute hematoma is seen by non-contrast imaging as an area of high density. CT can detect acute intracerebral blood as small as 2mm, due to contrast between high density of blood and low density of surrounding brain (arrows). |
 |
|