Abscess: Cavitary mass involving the brain parenchyma with infectious etiology.
Encephalitis: Encephalitis is a diffuse non focal parenchymal inflammatory disease, usually with viral etiology, e.g., herpes encephalitis.
Cerebritis: Early stage of brain infection. Untreated cerebritis can lead to abscess.
Meningitis: Inflammatory infiltration of the pia matter, arachnoid and cerebrospinal fluid.
Ventriculitis (Ependymitis): Infection involving the ependymal lining of the ventricle.
Empyema: Subdural empyema is a collection of pus within the subdural space.
Epidural empyema is a collection of pus within the epidural space.
AIDS - HIV related infections (immunocompromised patients)
- HIV encephalitis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Cryptococcosis
- Tuberculosis
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) ependymitis
Brain Abscess
Infection involving the brain parenchyma.
Ring enhancing mass with a central cavity that involves the brain parenchyma with surrounding edema and mass effect. The collagen capsule surrounding the abscess cavity enhances with contrast (ring enhancement). The central cavity of the mass contains liquified necrotic material, inflammatory debris and pus in pyogenic abscess.
Etiology:
- Bacterial pyogenic: Staphylococcus, steptococcus, pneumococcus
- Granulomatous: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Fungal: Cryptococcosis, aspergillosis, mucormycosis
- Parasitic: Toxoplasmosis, cysticercosis
CT/MR imaging findings of typical brain abscess:
- Enhancing ring lesion
- Smooth ring
- Rim thick towards cortex
- Rim thin towards ventricles
- On diffusion wtd image (DWI) the central cavity appears bright and lights up like a bulb
- Can incite surrounding edema resulting in mass effect and even brain herniation
- Daughter abscesses
Differential diagnosis for brain abscess:
- High grade gliomas: Glioblastoma (GBM) centrally necrotic tumor with irregular peripheral enhancement.
- Clinical presentation is usually with history of seizures and gradual focal neurological deficits.
- On diffusion wtd image (DWI) the central necrotic portion of GBM is not as bright as abscess activity.
Metastasis:
- Ring enhancing tumor with central cyst, can mimic brain abscess.
- Clinical history of primary tumor site such as lung, breast, thyroid, renal cell carcinoma and melanoma offers an important clue to the diagnosis of metastasis.
- On DWI the central cystic component of metastasis is not as bright as abscess cavity containing pus.
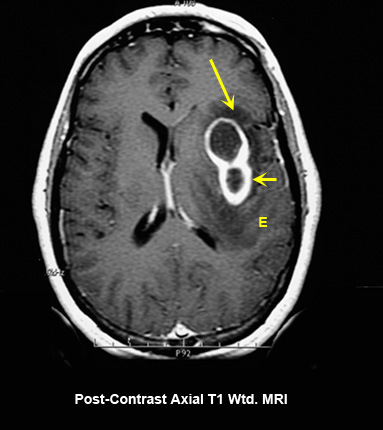
Figure 1A
Pyogenic abscess
Case 1
Imaging findings:
Fig 1A: Post-contrast axial T1 wtd. MRI
- Post-contrast axial T1 wtd. image which demonstrates a ring enhancing lesion (large arrow) in the left lateral basal ganglia region surrounded by edema (E).
- Small arrow points to a daughter abscess.
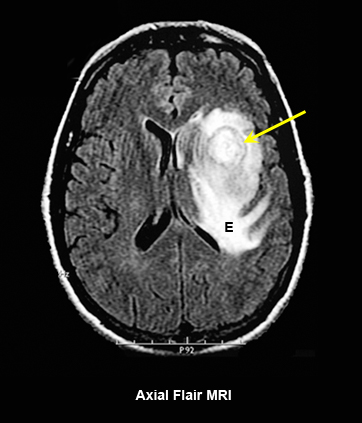
Figure 1B
Pyogenic abscess
Case 1
Imaging findings:
Fig 1B: Axial Flair MRI
- The edema (E) surrounding the abscess cavity is well seen in flair image.
- Large arrow points to the abscess cavity less clearly seen when compared to contrast MRI (Fig 1A).
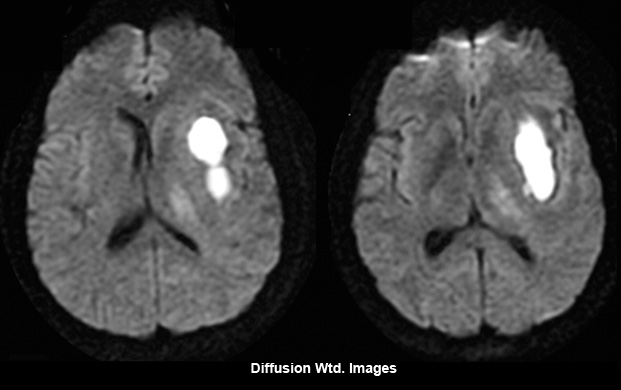
Figure 1 C
Pyogenic abscess
Case 1
Imaging findings:
Fig 1C: Diffusion wtd Images
- Diffusion wtd image shows central area within the abscess cavity filled with pus seen as an area of bright signal intensity lighting up like a bulb.
Bright signal intensity within the abscess cavity containing pus, seen on diffusion weighted image (DWI) is due to restriction of movement of H20 molecules from extracellular space to intracellular space.
This is a unique feature of pyogenic abscess that helps to differentiate brain abscess from glioblastoma and metastasis.
Most important feature to remember.
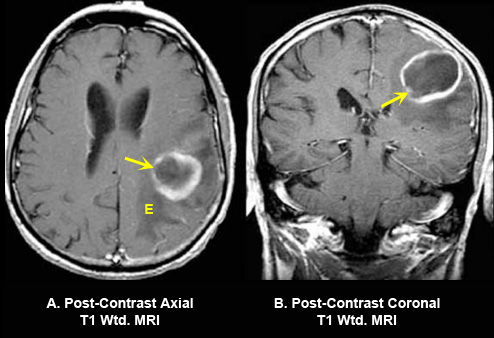
Figure 2
Pyogenic abscess
Case 2
Imaging findings:
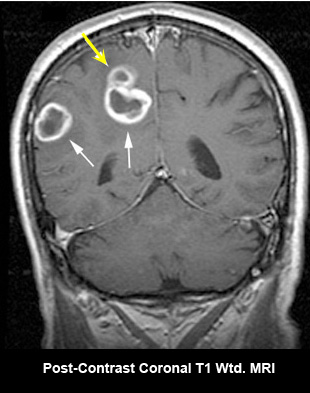
Fig 2A: Post-contrast axial and coronal T1 wtd. MRI
- An enhancing ring lesion within the left posterior frontal lobe.
- Good demonstration of thinning of the capsule towards the ventricle (arrow in A, B).
- Edema (E) surrounds the abscess which is hypointense on T1 wtd. image.
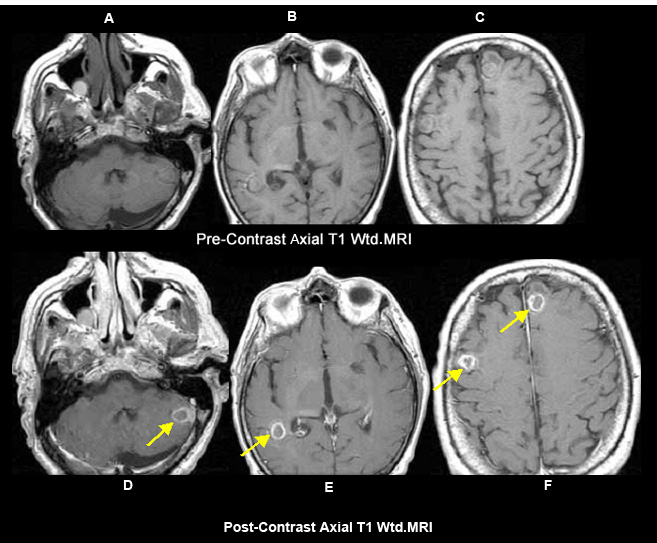
Figure 3
Fungal abscess - Non-Pyogenic abscess
Case 3
Imaging findings:
Figure 3 A, B, C: Pre-contrast axial T1 wtd. MRI
Figs 3 D, E, F: Post-contrast T1 wtd. MRI:
- Yellow arrow points to abscess cavity within the left cerebellar hemisphere (arrow in D), right posterior temporal lobe (arrow in E) and frontal lobes (arrows in F).
A case of fungal abscess in an immunocompromised patient.
Multiple enhancing ring lesions in an immunocompromised patient
Appropriate history and clinical findings are needed to aid in the etiology of abscess.