Short arrow points to amorphous material within the yolk sac in the featal pole.
In a patient who is in the high-risk group for developing an ectopic pregnancy, screening with quantitative beta-HCG, progesterone, and sonography should be done as soon as pregnancy is confirmed.
Vaginal sonography: This can be used to detect uterine gestation as early as 1 week after missed menses with a serum beta-hCG is higher than 1500 mIU/mL. An empty uterus with a serum beta-hCG of 1500 mIU/mL or higher was 100 percent accurate in identifying an ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancies can be missed, though, when a tubal mass is small or obscured by bowel. For identifying an ectopic pregnancy, the sensitivity is 96% and specificity is 99% when free peritoneal fluid is identified. However, when there is a tubal mass, the sensitivity is 81% and the specificity if 99%.
Vaginal Color and Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: This consists of identifying a uterine or extra uterine site of vascular color in a “ring of fire” pattern (characteristic placental shape) and a high-velocity low-impedence flow pattern that is compatible with placental perfusion. If this pattern is seen outside the uterine cavity and also appears “cold” with respect to blood flow, the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is apparent.
An empty uterus and an ectopic pregnancy are seen with visualization of an adnexal mass separate from two clearly identified ovaries
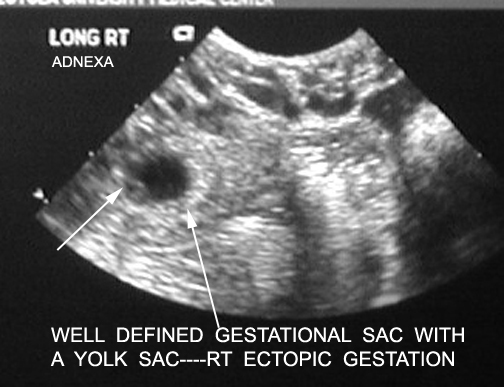
| Right ectopic.
Short arrow points to amorphous material within the yolk sac in the featal pole. |
 |
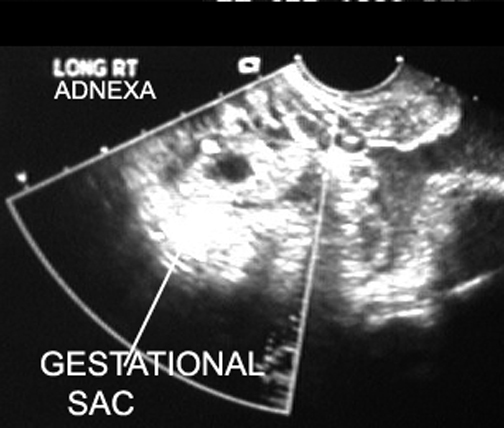
| Gestational sac in adnexa |  |
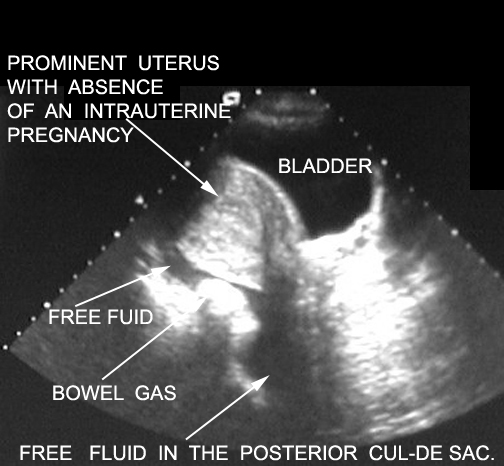
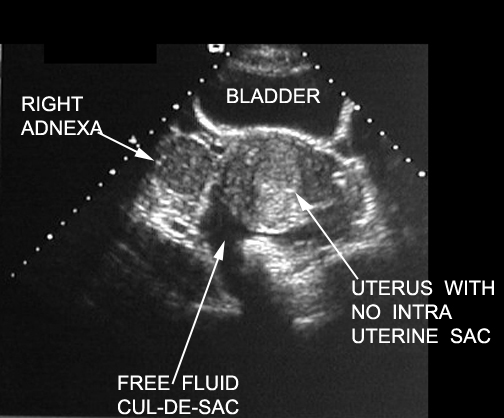
| No intrauterine pregnancy. Increased serum HCG. |  |
| No intrauterine pregnancy. Free fuid may be from follicualr rupture. Serum HCG is not increased. |  |
| Normal |  |